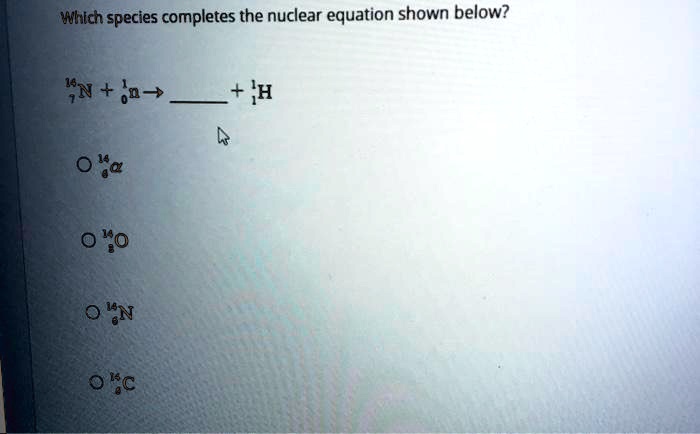
Which species completes the nuclear equation shown below? This question sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the intricacies of nuclear reactions, we will uncover the secrets that lie within these enigmatic equations and identify the missing species that completes the puzzle.
Nuclear equations, with their intricate interplay of atomic nuclei, provide a fascinating window into the realm of nuclear chemistry. By understanding the components and structure of these equations, we gain insights into the fundamental forces that govern the behavior of matter at its most basic level.
Nuclear Equations: Which Species Completes The Nuclear Equation Shown Below
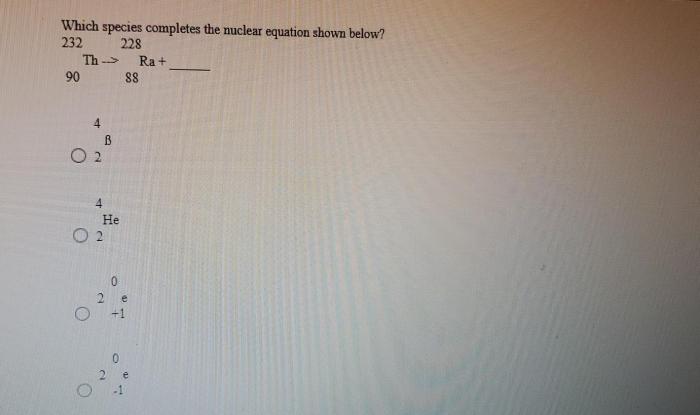
Nuclear equations are symbolic representations of nuclear reactions, which involve changes in the atomic nuclei of atoms. They provide a concise way to describe the transformation of one set of nuclei into another.Nuclear equations consist of three main components: the reactants, the products, and the balancing coefficients.
The reactants are the nuclei that undergo the reaction, while the products are the nuclei that are formed as a result of the reaction. The balancing coefficients are numbers that ensure that the total number of protons and neutrons on both sides of the equation is the same.
Identifying the Species Completing the Nuclear Equation
Given a nuclear equation, the missing species can be identified by considering the conservation laws of nuclear reactions. These laws state that the total number of protons and neutrons must be the same on both sides of the equation.To complete the nuclear equation, the missing species must have an atomic number and mass number that satisfy the conservation laws.
This can be done by using the atomic and mass numbers of the known species in the equation.
Methods to Determine the Missing Species
There are several methods that can be used to determine the missing species in a nuclear equation. One common method is to use the conservation laws of nuclear reactions. These laws state that the total number of protons and neutrons must be the same on both sides of the equation.Another
method to determine the missing species is to use the atomic and mass numbers of the known species in the equation. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
By using the atomic and mass numbers of the known species, it is possible to determine the atomic and mass numbers of the missing species.
Characteristics of the Missing Species, Which species completes the nuclear equation shown below
The missing species in a nuclear equation typically has properties that are similar to the other species in the equation. For example, if the other species in the equation are radioactive, then the missing species is also likely to be radioactive.The
missing species can also affect the overall nuclear reaction. For example, if the missing species is a neutron, then the reaction may be a neutron-induced reaction. If the missing species is a proton, then the reaction may be a proton-induced reaction.
FAQ Corner
What is a nuclear equation?
A nuclear equation is a symbolic representation of a nuclear reaction, showing the changes that occur to the atomic nuclei involved.
How do I identify the missing species in a nuclear equation?
To identify the missing species, use conservation laws and the atomic and mass numbers of the known species in the equation.
What is the significance of the missing species in nuclear chemistry?
The missing species plays a crucial role in determining the overall outcome and energy release of the nuclear reaction.